Breast Cancer (Part One)
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops in the glandular tissue, it is divided into two main types:
- Ductal carcinoma (which develops in the lactiferous ducts), most breast cancers are of this type.
- Lobular carcinoma develops in the breast lobule, part that produces milk.
Breast cancer can be invasive and non-invasive (invasive – has spread from the lactiferous ducts or lobules to the rest of the breast, non-invasive – means it has not spread to the rest of the breast, the latter is otherwise called “in situ”).
Most breast cancers are estrogen sensitive, which means that the estrogen hormone causes the growth of breast cancer. These tumors have estrogen receptors on the surface of their cells. They are called estrogen receptor-positive cancers or ER-positive cancer.
A portion of women have a type of breast cancer called HER2-positive. HER2 refers to a gene that helps cells grow, divide, and repair. When cells (including cancerous cells) have too many copies of this gene they grow faster. Women with HER2-positive cancer have a more aggressive disease and a higher risk of recurrence than women who do not have this type.
However, this can change thanks to specific treatments against HER2. One in eight women is affected by breast cancer.
Risk factors for breast cancer are:
factors which cannot be changed such as:
- age with the increase of age the incidence of breast cancer increases.
- genes if the person is a carrier of the genetic mutation BRCA 1 and BRCA 2.
(Carrying these genes increases the probability of breast cancer by 80%.) - personal factors such as the start of menstruation under the age of 12 or the start of menopause after the age of 55.
Other risk factors for breast cancer are giving birth to the first child after the age of 30, tobacco and alcohol, there is also a link between the use of oral contraceptives and breast cancer.
Signs of breast cancer are:
- A lump or palpable nodule in the breast.
- Change in size or shape of the breast.
- Discharge from the nipple.
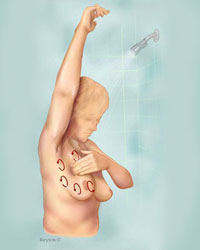
Given these, self-examination of the breast has special importance. Self-examination of the breast is a good opportunity to discover breast cancer in its early stages.
During the self-examination of the breast, you should keep in mind:
- make it a habit to self-examine your breast every month so that you become familiar with the way your breast looks and feels.
- Self-examination is done a few days after the menstrual cycle ends (days in which the breast is less painful and less swollen). If you no longer have periods, choose a day of the month that can be easily remembered, like the first day of the month or the last day of the month.
Steps to follow during self-examination.
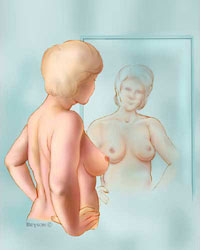
Step I. Start by looking at your breast while standing in front of the mirror, with straight shoulders and hands on the hips.
You should evaluate the size, shape, and color of your breast.
If you notice any of the following changes, immediately go to the doctor.
- Dimpling, swelling, wrinkling of the skin.
- The nipple has changed position (it is inverted instead of protruding).
- Redness, swelling.